

CPU-frequency scalingĬpufreq is a module that dynamically adjusts the CPU frequency. This section introduces performance tuning based on the classified kernel subsystems. For detailed usage of the BCC toolkit, see BPF Compiler Collection (BCC). Compared with kprobe, BPF provides higher security and is more suitable for the production environments. Compared with perf/ftrace, BPF provides programmability and smaller performance overhead. Therefore, you can choose proper tools to conduct an in-depth analysis based on the results in In 60 seconds. Starting from CentOS 7.6, the Linux kernel has supported Berkeley Packet Filter (BPF).
#Linux kernel tuning software#
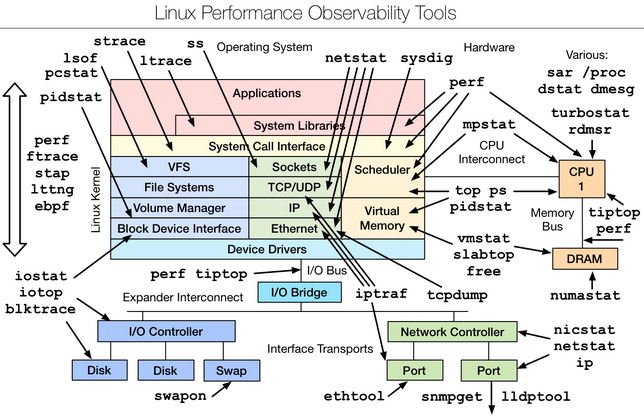
Perf is an important performance analysis tool provided by the Linux kernel, which covers hardware level (CPU/PMU, performance monitoring unit) features and software features (software counters, trace points). You can analyze outputs of the following list items to troubleshoot most common performance issues.įor detailed usage, see the corresponding man instructions. All tools used can be obtained from the official release of Linux. Linux Performance Analysis in 60,000 Milliseconds is published by the author Brendan Gregg and the Netflix Performance Engineering team. This section lists common methods for performance analysis. System tuning must be based on the results of system performance analysis. Fully test all the changes in the test environment before applying them to the production environment.Therefore, before tuning the system, back up all the user data and configuration information. Adjusting the performance of a particular subsystem might negatively affects other subsystems. The default configuration of the CentOS 7 operating system is suitable for most services running under moderate workloads.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
